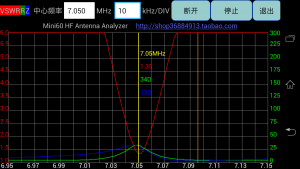
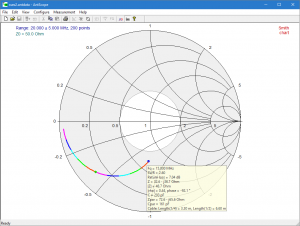
Backing out transmission line
Often we make measurements through a section of transmission line, and the measurements are wrt the reference plane, which for many analysers is the connector on the instrument.
Some analysers, or their associated software allow the effects of the transmission line to be backed out.
Above is a Smith chart view of measurement of a test antenna through some length of RG58. The antenna will have R<50Ω at minimum VSWR, so the angle of the complex reflection coefficient Γ will be close to 180° at the feed point. Antscope uses a different notation, but shows here the angle at the point of measurement to be -15.1°, so we need to increase it by 180–15.1=195.1°, which will take about half that electrical length of line, 97.6°. From TLLC, I calculate the length involved is 7.6m of RG58, which is an estimate that gives a starting point for backing out the cable. Continue reading Exploiting your antenna analyser #11